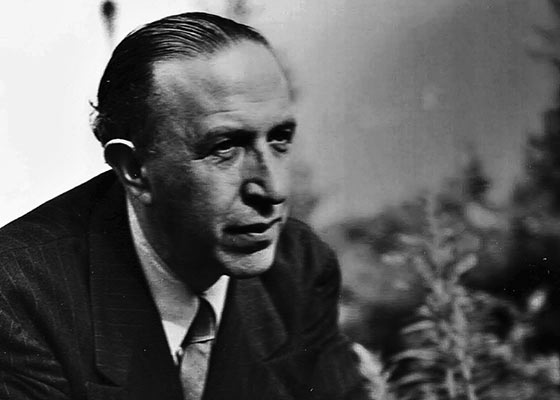
El Lisitski
(English)
Born Lazar Markovich (El) Lissitzky (Ла́зарь Ма́ркович Лиси́цкий) in 1890 to an educated middle-class Jewish family in Pochinok, Smolensk Province, Russia. He grew up in Vitebsk, a small Jewish town in Belorussia, where he took art lessons in 1903 from Russian painter Iurii (Yehuda) Moiseevich Pen, who also taught Marc Chagall. In 1909, after being turned down by the St. Petersburg Academy of Art, Lissitzky left Russia for the first time to enroll at the Technische Hochschule in Darmstadt, Germany, where he studied architectural engineering. During his studies, in 1912 he traveled in Germany and also to France and Italy, but was forced to return to Russia during the summer of 1914, after the outbreak of World War I. He enrolled as a student of engineering and architecture at the Riga Polytechnical Institute [Rizhskii politekhnicheskii institut], temporarily quartered in Moscow, and received his diploma on 3 June 1918 with the degree of engineer-architect. In 1915-16 he worked in various architectural offices in Moscow and St. Petersburg.
In 1916 Lissitzky became deeply involved in a Russian national movement to create a revival of Yiddish culture for modern Russian Jews. With the artist Issachar Ryback, he set off on an expedition organized by the Jewish Historical and Ethnographic Society [Evreiskoe istorichesko-etnograficheskoe obshchestvo] to study and record the ornamentation and inscriptions in synagogues located along the Dnieper River. Following the February Revolution of 1917, Lissitzky moved from Moscow to Kiev where he devoted himself to the illustration of Yiddish books, especially for children, and organised and submitted work for exhibitions of Jewish art in Moscow. In early 1919, he helped found the publishing house Kultur-Lige, which became a leading force in the dissemination of Yiddish culture in Ukraine. Toward the end of his stay in Kiev, Lissitzky worked for the art section of the local branch of IZO Narkompros.
Vitebsk and Moscow (1919-21)
Lissitzky’s move in July 1919 from the relative isolation of the Bolshevik-controlled city of Kiev back to Vitebsk brought with it a shift in focus from Yiddish culture to architecture and book design. At the invitation of Marc Chagall, Lissitzky began a new position teaching architecture, graphic arts, and printing at the Vitebsk Popular Art Institute. In September, he was joined by Kazimir Malevich, whose system of nonobjective art, suprematism, inspired Lissitzky to take up painting and to invent his own form of abstract art, which he named Proun [Proekt utverzhdenia novogo; Project for the Affirmation of the New] in 1920. Propaganda also became a more overt part of Lissitzky’s artistic mission at this time; during the civil war, he worked in the suprematist collective UNOVIS [Affirmers of the New Art] as a designer of agitational posters meant to incite workers back to the factory benches and to rally Jews around Bolshevism.
After disagreements between Chagall and Malevich led to the disbandment of the Institute in 1921, Lissitzky returned to Moscow to teach architecture at the newly established VKhUTEMAS. This was a period of great artistic ferment and debate in Moscow. Lissitzky’s arrival coincided with the emergence of the radical First Working Group of Constructivists, which advocated a utilitarian and socialist platform of art for industry. In September 1921, at INKhUK, Lissitzky put forth his own program in an important lecture, outlining the connections between suprematist painting and the principles of space and construction in his Proun works.
Germany and Switzerland (1921-25)
In December 1921, Lissitzky left Russia for Berlin, by way of Warsaw, dispatched by the Soviet government to establish cultural contacts between Soviet and German artists. In 1922 he collaborated with the Russian writer Ilya Ehrenburg on producing two issues of the short-lived periodical Veshch/Objet/Gegenstand; met the typographer Jan Tschichold who became his life-long friend. In May 1922 Lissitzky participated in the Congress of International Progressive Artists in Düsseldorf; followed by the Congress of the Constructivists and Dadaists in Weimar in September, where he met the Dada artist Kurt Schwitters. He had a minor role in setting up the First Russian Art Exhibition in Berlin in October, when he also met Sophie Küppers, who had been the artistic director of the Kestner Society in Hanover, founded by her recently deceased husband Paul Erich Küppers to support and promote the German avant-garde. In December 1922 he delivered an important lecture in Berlin on Soviet art, the next year followed by the lectures in Rotterdam, Utrecht, The Hague and at the Kestner Society. In 1923, Lissitzky also shortly joined the editorial board of Hans Richter’s journal G; became a member of the De Stijl group; and joined ASNOVA (Association of the New Architects), an organization founded in Moscow by Nikolai Ladovsky, Nikolai Dokuchaev and Vladimir Krinsky, assuming responsibility for developing connections with foreign architects.
In October 1923 he was taken ill with acute pneumonia, a few weeks later diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis, and in February 1924 relocated to a sanatorium near Locarno, Switzerland, where, with the help of his future wife Sophie, he produced publications and photographs at a remarkable pace: edited the architectural review ABC: Beiträge zum Bauen with Dutch architect Mart Stam and Swiss architect Emil Roth; produced advertising designs for Gunther Wagner’s Pelikan office supply company; and with the technical help of Roth, began work on the Wolkenbügel [Cloud Iron], a horizontally expanding skyscraper intended for the Nikitsky Square in Moscow. In November 1924 the Swiss authorities turned down his request to renew his visa, but grant him a six-month extension “on humanitarian grounds.”
Exhibition work in Germany and Russia
In June 1925 Lissitzky returned to Moscow via St Petersburg. In January 1926 he was appointed head of the Department of Furniture and Interior Design for the wood and metal workshop at VKhUTEMAS. Later in June he received assignment from Narkompros to travel to Dresden, Rotterdam, Utrecht, Hamburg, and Lübeck to study modern architecture. In Germany, he was commissioned by the directorate of the International Art Exhibition in Dresden to design the Raum für konstruktive Kunst [Room for Constructivist Art] (1926), and by Alexander Dorner to design the Kabinett der Abstrakten [Abstract Cabinet] for the Provinzialmuseum (Sprengel Museum) in Hanover (1927–28). In collaboration with Ladovsky, Lissitzky published the single issue of the architectural review ASNOVA in Moscow, 1926.
By 1927, with the success of his design for the All-Union Printing Trades Exhibition in Moscow, Lissitzky had became a much sought-after propagandist for the Stalinist regime, realising the Soviet Pavilion at the International Press Exhibition in Cologne (1928), the Soviet Room at the Film and Photo Exhibition in Stuttgart (1929), the Soviet Pavilion at the International Hygiene Exhibition in Dresden (1930), the Soviet section at the International Fur Trade Exhibition in Leipzig (1930), and the Gorky Park of Culture and Rest in Moscow (1931).
On 27 January 1927 Lissitzky married Sophie Küppers; his son, Jen, was born on 12 October 1930; and the next year Sophie’s older sons come to Russia to live with her and Lissitzky in the village of Khodnya, thirty miles from Moscow. During a 1928 vacation in Austria and Paris Lissitzky met Piet Mondrian, Fernand Léger and Le Corbusier.
Later years
In 1932 Lissitzky signed his first contract with the editors of USSR im Bau [USSR in Construction], a Soviet propaganda publication intended for Western audiences and published in Russian, English, German, and French; became one of the principal artists for the journal, along with Aleksandr Rodchenko, Varvara Stepanova, and Solomon Telingater; designed seventeen issues, ten of them in collaboration with Sophie Küppers. In 1934 he was appointed chief artist for the Agricultural Exhibition of the Soviet Union in Moscow. During 1935-36 Lissitzky was frequently hospitalized; convalesced in a sanatorium in the Caucasus. In 1940 he was appointed chief artist for the Soviet Pavilion at the Belgrade International Exhibition, a project left unfinished due to the outbreak of World War II. In 1941 he worked on anti-Nazi posters and other war-related projects until his death in Moscow on 30 December.
(Spanish)
Polchinok (Rusia) 1890 – Moscú, 1941, fue un artista ruso, diseñador, fotógrafo, maestro, tipógrafo, y arquitecto.
Fue una de las figuras más importantes de la vanguardia rusa, contribuyendo al desarrollo del suprematismo junto a su amigo y mentor, Kazimir Malévich, y diseñó numerosas exposiciones y obras de propaganda para la Unión Soviética. Se le considera uno de los principales representantes del arte abstracto y pionero en su país del constructivismo. Su obra influyó grandemente en los movimientos de la Bauhaus, el constructivismo, y De Stijl, y experimentó con técnicas de producción y recursos estilísticos que posteriormente dominaron el diseño gráfico del siglo XX. En español, su apellido también se ha transliterado como Lissitski, mientras que en inglés y otros idiomas se suele transliterar como Lissitzky. El diminutivo El viene de Eliazar, una variante de su nombre de pila.
Toda la carrera de Lisitski se guio por la creencia de que el artista podía ser un agente del cambio social, lo que más tarde resumió en su dicho, “das zielbewußte Schaffen” (La creación orientada a un objetivo).1 Era judío, y comenzó su carrera con ilustraciones de libros infantiles en yidis, en un esfuerzo por promover la cultura judía en Rusia, un país que estaba pasando por un enorme cambio en aquella época, y que acababa de revocar sus leyes antisemitas. A los quince años de edad comenzó a impartir enseñanza, una tarea a la que se dedicó durante la mayor parte de su vida. A lo largo de los años, enseñó desde diversos cargos, escuelas, y medios artísticos, difundiendo e intercambiando ideas a un ritmo rápido. Llevó consigo su ética cuando trabajó con Malévich liderando el grupo artístico suprematista UNOVIS, donde desarrolló una serie suprematista variante propia, los Prouns, y más aún todavía en 1921, cuando asumió un cargo como embajador cultural de Rusia en la Alemania de Weimar, trabajando con una serie de figuras destacadas, a las que influyó, tanto de la Bauhaus como del movimiento De Stijl. Durante el resto de su vida, realizó innovaciones significativas y cambios en los campos de la tipografía, diseño de exposiciones, fotomontaje, y diseño de libros, produciendo obras respetadas por los críticos y obteniendo el aplauso internacional por sus diseños de exposiciones. Así siguió hasta su muerte, produciendo su última obra en 1941, un cartel de propaganda soviética que instaba al pueblo a construir más tanques para la lucha contra la Alemania nazi.